Transarterial Radioembolization (TARE) is a sophisticated palliative option for treating liver cancers, such as Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Cholangiocarcinoma.
A PICC line, or peripherally inserted central catheter, is a slender, flexible tube inserted into a vein in the arm, leg, or neck, with its tip positioned in a major vein near the heart.
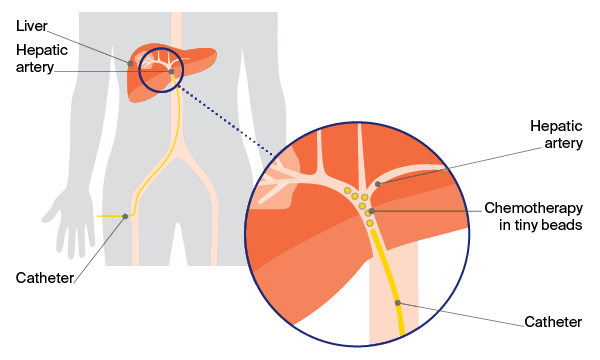
TACE is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat liver cancer. It involves delivering chemotherapy directly into the tumor’s blood vessels along with a blocking agent to cut off its blood supply.
Microwave ablation (MWA) is a minimally invasive technique that uses microwave energy to destroy cancerous tumors. It is an excellent option for patients who are not candidates for surgery or have tumors that are too large or challenging to remove surgically.
PTBD is a medical procedure used to diagnose or treat bile duct obstructions. The goal is to identify the site of the blockage and/or place a temporary catheter to drain bile. This procedure is ideal for patients seeking to avoid surgery or those for whom surgery poses significant risks, as it typically involves fewer complications than surgical options.
TACE Procedure for Liver Cancer
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
TACE is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat liver cancer. It involves delivering chemotherapy directly into the tumor’s blood vessels along with a blocking agent to cut off its blood supply.
Benefits
- TACE can help control cancer, alleviate symptoms, and extend the patient’s life.
- It is effective for treating tumors that are too large for surgery or radiation therapy.
- TACE can also target cancers that have metastasized to the liver.
Preparation
- Blood tests may be performed to assess blood counts, as well as liver and kidney function.
- A mild sedative may be administered to help the patient feel relaxed during the procedure.
