Permacath insertion is a minimally invasive procedure in which a catheter is placed into a blood vessel in the neck or upper chest. This catheter is used for hemodialysis, a vital treatment for patients with kidney disease.
Fistuloplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to clear blockages in an arteriovenous fistula, enabling access for dialysis without the need for surgery. The blockage is treated by inflating a specialized balloon or device, which improves blood flow through the fistula.
TEVAR is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat conditions affecting the thoracic aorta, such as aneurysms or dissections. Located in the chest, the thoracic aorta is a critical blood vessel, and TEVAR offers a less invasive alternative to open surgery, providing benefits like shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times.
A peripheral angiogram, also known as extremity angiography, is a diagnostic test that uses X-rays and contrast dye to identify narrowed or blocked arteries supplying blood to the legs, feet, arms, or hands.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a vein located deep within the body, most commonly in the legs, arms, or other areas.
Varicocele embolization is a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure designed to treat varicoceles—enlarged veins in the scrotum. It is an effective option for addressing varicoceles that cause pain, swelling, or infertility.
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that typically appear on the legs due to increased pressure on the veins. This condition is caused by the weakening of vein walls or malfunctioning valves, which leads to improper blood flow.
VenaSeal provides fast and effective relief from varicose veins. This minimally-invasive, outpatient procedure offers a more comfortable experience with shorter recovery times.
Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE) Treatment In Delhi, India
What is it?
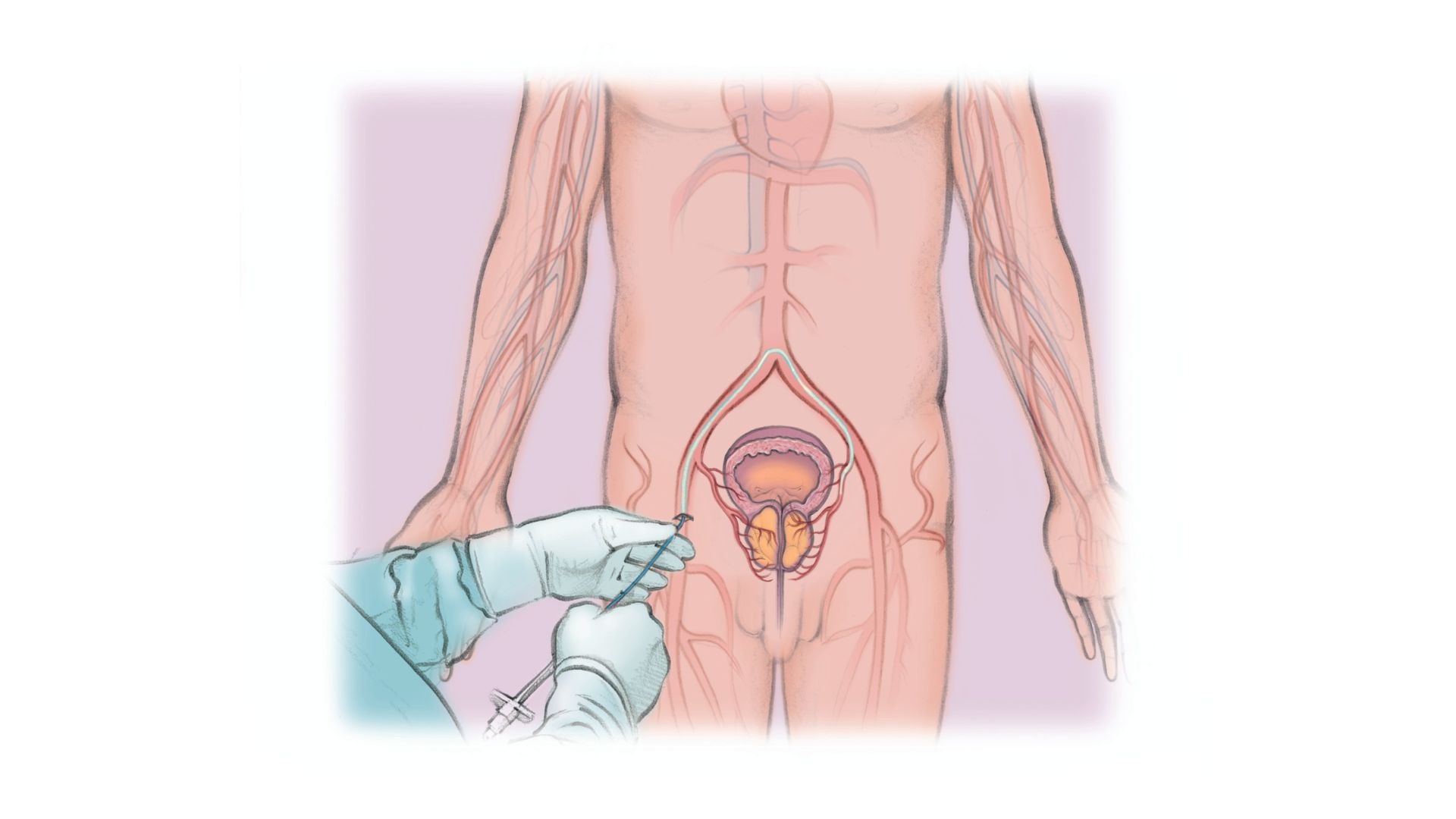
Prostatic artery embolization (PAE) is a minimally invasive treatment to improve lower urinary tract symptoms caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland and is the most common benign tumor found in men.
The PAE procedure is performed by an interventional radiologist (IR), a doctor who uses X-rays and other advanced imaging to see inside the body and treat conditions without surgery.
Why (Indications)?
As the prostate enlarges, it may partly block the urethra, causing symptoms such as:
- Urinary incontinence, which can range from some leaking to complete loss of bladder control
- Irritative voiding symptoms
- Increased urinary frequency, urgency, and pain upon urination

How do I know if PAE is right for me?
The PAE procedure is for candidates who are either ineligible or not interested in traditional surgery. An exam with an interventional radiologist can determine if you are a candidate for PAE. At this appointment, you may be asked how often you have urinary symptoms of BPH, how severe they are, and how much they affect your quality of life.
Why not (Contraindications)?
Patients are excluded from treatment if they have malignancy, renal insufficiency, bladder stones, a neurogenic bladder (a neurologic disorder that may affect bladder function), urethral stricture, an active urinary tract infection, or prostatitis.
What you are to do before procedure (Preparation)?
- Book prior appointment if elective or get admission in causality if emergency
- Lab investigation (*PT/INR, CBC, Serum Creatinine, Viral markers)and previous records. An MRI or ultrasound of the prostate gland.
- Urine test (urinalysis)
- In some cases, a PSA (prostate specific antigen) test is done to rule out prostate cancer.
- 4-6 Hours fasting.
- If you are on blood thinner like Aspirin inform during appointment.
- One accompanying person
- Need to sign a consent form for procedure
What happens during PAE?
- PAE is performed through a small catheter inserted by your interventional radiologist into the artery in your groin.
- The interventional radiologist will then guide the catheter into the vessels that supply blood to your prostate.
- An arteriogram (an X-ray in which dye is injected into the blood vessels) is done to map the blood vessels feeding your prostate.
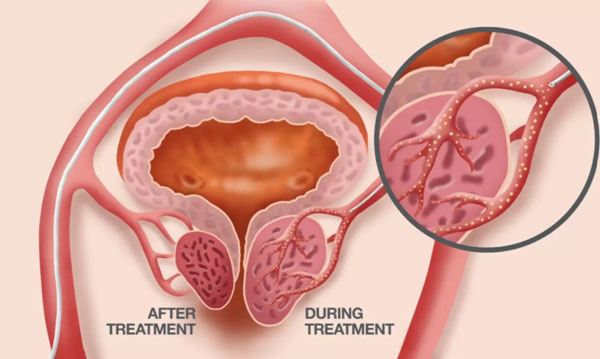
- The agent (glue/particles) is injected through the catheter and into the blood vessels that feed your prostate to reduce its blood supply.
- The interventional radiologist will move the catheter in order to treat the other side of your prostate, repeating the steps above.
- Following this procedure the prostate will begin to shrink, relieving and improving symptoms usually within days of the procedure.
Approx. Stay in hospital?
We have very fast and competent working team (Consultant, fellow, clinical assistant, technician and ward assistant) which provide you comfortable atmosphere and ease your nerves. Usual time of stay is around 1 day.
Complications
Minor complications include dysuria (9%), urinary tract infection (7.6%), microscopic hematuria (5.6%), acute urinary retention (2.5%), and rectal bleeding (2.5%)
Resume to work?
You can resume your work after 1 day if existing disease allows.
Results?
Cumulative rates of clinical success are 80- 85%.
For any Queries or Appointment please call
