Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology (USG-guided FNAC)) is a diagnostic technique that utilizes ultrasound imaging to place a needle into a mass to collect cells for examination. This procedure is swift, safe, and reliable, allowing for the diagnosis of various medical conditions.
Ultrasound-guided biopsy is a type of image-guided biopsy, generally conducted by a radiologist. It is the most prevalent form of image-guided biopsy, providing the advantage of convenience along with real-time visual monitoring.
A CT-guided biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure where a CT scan helps direct a needle to collect a tissue sample from an unusual area within the body.
Drainage catheter placement is a medical procedure that consists of inserting a slender, flexible tube into the body to eliminate excess fluid or air. This tube can be introduced into various areas, such as the abdomen, liver, kidney, chest, or other locations.
Pain management is a healthcare discipline that employs various treatments to alleviate pain and enhance overall quality of life. It can address both sudden pain, as in the case of a fracture, and ongoing pain associated with chronic conditions.
Percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) is a minimally invasive technique that allows urine to be drained from the kidney by placing a catheter through the skin. This procedure is beneficial for addressing urinary obstructions, kidney stones, and various other medical issues.
Antegrade DJ stenting is a procedure that involves placing a stent into the kidney and ureter to alleviate a blockage, facilitating normal urine drainage. An interventional radiologist carries out the procedure using imaging guidance.
Drainage Catheter Placement
Drainage catheter placement is a medical procedure that consists of inserting a slender, flexible tube into the body to eliminate excess fluid or air. This tube can be introduced into various areas, such as the abdomen, liver, kidney, chest, or other locations.
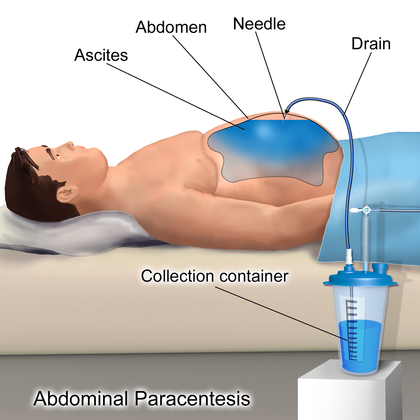
During the procedure, your physician will insert the catheter through your skin into the spot where fluid has accumulated. They will utilize imaging techniques like fluoroscopy (real-time X-rays), a computed tomography (CT) scan, or ultrasound to maneuver the catheter into the correct position. Afterward, they will attach it to your skin using a suture.
Typically, this procedure lasts less than one hour.The catheter is taken out when your symptoms improve, lab results return to normal, and there is no further drainage.
