DSA provides detailed images of the blood vessels in the brain to assess any issues with blood flow. The procedure involves inserting a small, thin catheter into an artery in the leg, guiding it through the vessels to the brain. A contrast dye is then injected, and X-ray images are captured of the blood vessels.
Aneurysm coiling, also known as endovascular coiling, is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat brain aneurysms. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into an artery in the groin and carefully guided to the brain artery containing the aneurysm.
Mechanical thrombectomy is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to remove blood clots from the brain after an ischemic stroke. A small incision is made in the groin, through which thin tubes (catheters) are guided to the clot.
AVM embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that targets and blocks abnormal blood vessels in an arteriovenous malformation (AVM). This treatment is particularly important for AVMs located in the brain, as they can lead to severe neurological damage if they rupture.
Mechanical Thrombectomy
Mechanical thrombectomy is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to remove blood clots from the brain after an ischemic stroke. A small incision is made in the groin, through which thin tubes (catheters) are guided to the clot. At the catheter’s tip, a specialized device is used to capture and remove the clot, restoring blood flow to the brain.
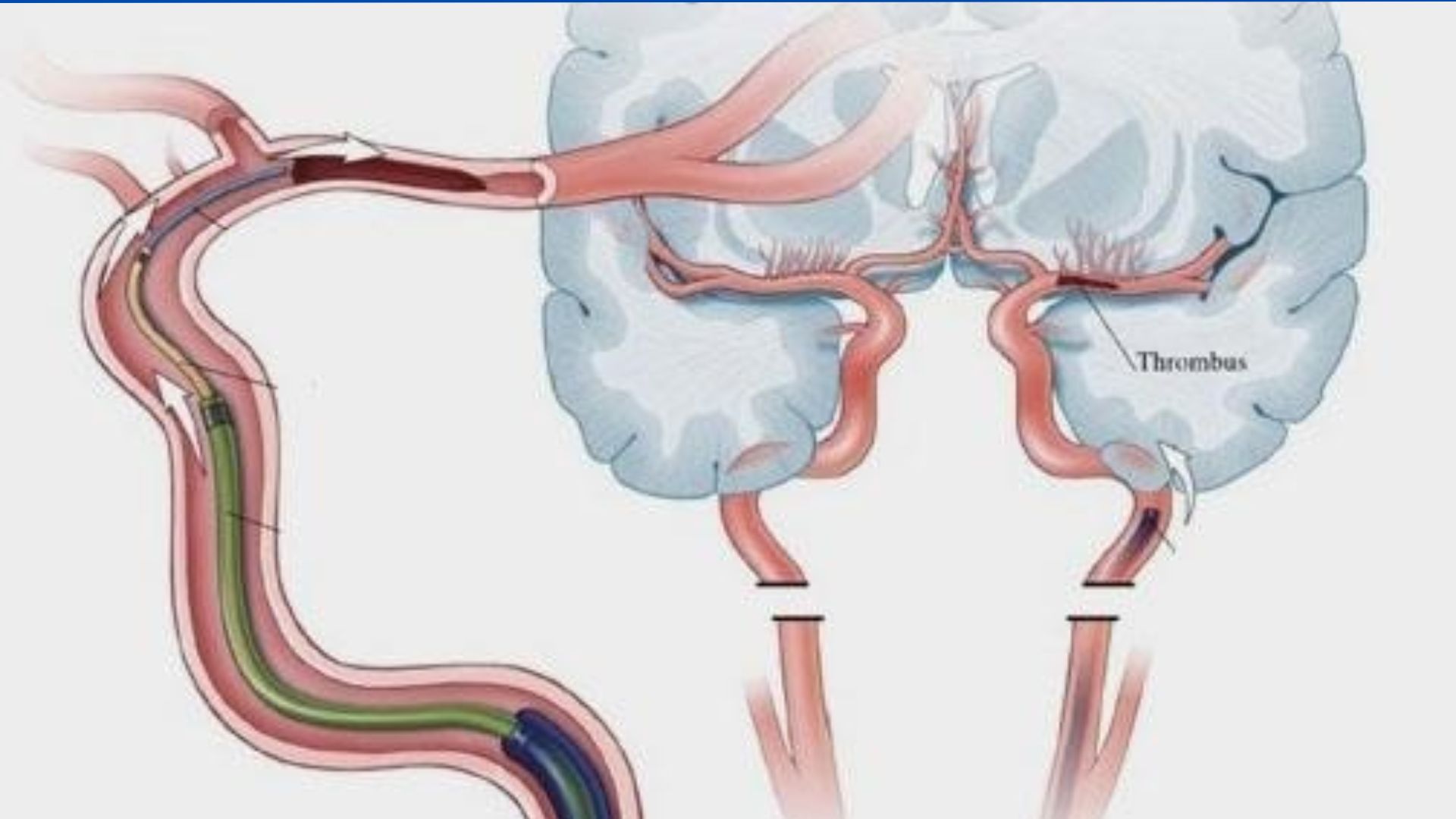
Mechanical Thrombectomy vs. Surgical Thrombectomy
Mechanical thrombectomy, or endovascular therapy, is less invasive compared to surgical thrombectomy. It eliminates the need for larger incisions and reduces disruption to the skull required in traditional surgical procedures.
Applications
- When standard treatment (thrombolysis) fails
- When the clot is too large for clot-busting drugs to dissolve
- For moderate to severe strokes
Benefits
- Significantly reduces the severity of disability
- Helps prevent and minimize long-term disability
